IASSIST Regional Report 2002-2003 European Region
Melanie Wright UK Data Archive May 2004
Introduction
The report that follows will begin with some observations on the demographics of IASSIST European membership. I will then report on a few of the many cross-national collaborations, after which will be country-by-country reports of national/institutional/individual activities. I have only included reports for those people/organisations/countries/projects from whom I have received information.
European membership
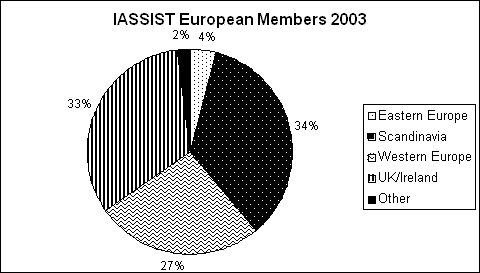
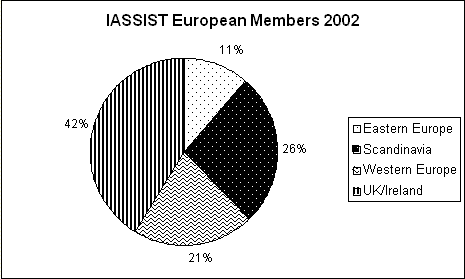
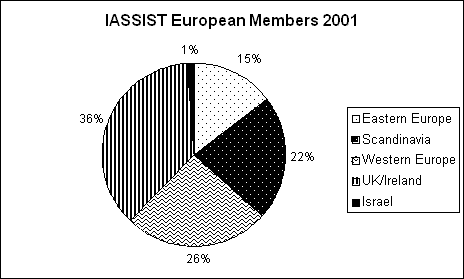
There are currently 49 IASSIST members from 13 countries “on the books” for the European region (down from 53/21 last year). We currently have no paid-up members from previously active countries: France, Greece, Hungary, Latvia, Romania, Russia, Slovakia, and Slovenia. The decrease in European membership from 2001’s high of 82 undoubtedly reflects the fact that the 2000/01 conference was held in Amsterdam, and the subsequent two conferences in North America. The geographic breakdown by sub-region across these to years is shown in the tables below. The Anglo-Scandinavian domination continues, most likely as a function of the fact that national funding for data service activities (including travel to conferences and membership in relevant organisations) is strongest in these countries. What is of concern to me is the significant drop in percentage coming from Eastern Europe. I am hopeful that this trend will reverse itself with the 2005 conference coming to relatively more accessible Edinburgh. This may, however, also be a reflection of the success of local networks such as EDAN, which provide much closer to home some of the same kinds of training and networking opportunities previously only available at IASSIST.
 {width=“480”
height=“273”}
{width=“480”
height=“273”}
 {width=“465”
height=“279”}
{width=“465”
height=“279”}
 {width=“464”
height=“279”}
{width=“464”
height=“279”}
Cross European Collaborations
MADIERA
Ken Miller writes: The MADIERA project is now half way through and on course to developing the tools and resources to produce an effective CESSDA gateway. Based on stable NESSTAR products the MADIERA portal will utilise “Google” type harvesting to incorporate the power of a multilingual thesaurus (ELSST) in both searches and resource evaluation.
This new front end to the NESSTAR suite of products will in itself become a standard product that can be used for other interoperability projects. The major changes to existing software will be in the publisher where allocation of terms from the thesaurus will be semi-automated and common variables stored with their associated keywords
The multilingual thesaurus now incorporates 8 European languages, namely English, French, German, Spanish, Danish, Finnish, Greek and Norwegian. It is hoped to double the number of concepts held in ELSST, to around 3,000, by the end of the project. Administrative procedures will also be put in place to ensure that the development and maintenance of the thesaurus continues beyond the end of the project.
MetaDater
Uwe Jensen writes: The MetaDater project (www.metadater.org) develops a Metadata Management and Production System for comparative social surveys repeated over space and time. The objectives and expected benefits of the project are to improve quality and richness of metadata by developing system procedures and relational information structures covering new exchange formats, standards and distributions platforms as well. It aims to provide data analysts and researcher with highly reliable and durable data and metadata documentation through the development of tools for efficient and economic production and management of those metadata by researchers (MD-COLL) and data services (MD-PRO).
Progress against workpackages since January 2003: [WP2 - Analysis of Requirements & User Needs]
The User analysis (WP2) refereed to the requirements and expectation to a MetaDater system and covered two potential user groups: Data Archivists and Researchers.
Data Archive Requirements & Expectations The principal contractors of the consortium (DDA, EKKE, NIWI, SSD, SIDOS, ZA) prepared substantial information on metadata processing and management according to the partner’s workflow. A general result was that the implications of the technical and functional differences between the existing systems and applications need deeper analytical work at WP 3 (Modelling the Database) to achieve a unique conceptual data model and WP4 (System Architecture) to judge the technical requirements to be considered during the design of MD-PRO (WP5) and MD-COLL (WP6).
Requirements & Expectations of researcher at research and fieldwork institutes The overall result of thirteen interviews on a metadata system covered some concepts and specific ideas to improve metadata capture already in the research phase. Broader attention was paid to facilities which support questionnaire development or metadata capture on the study design and the fieldwork. The project will consider to what extend these expectations can be covered developing the MD-COLL tool designed to this group of potential user.
[WP 3 - Modelling the Database] One central part of the project work in 2003 was to develop in WP3 a substantial data model for metadata of the domain as the first product of the project. As some of the most important entities (dataset, study etc) are defined through specific scientific procedures the process oriented perspective is of major importance in addition to the data/metadata perspective itself. Overall user and system analysis and data modelling are very closely related in this project. Although data modelling is usually described by the development of an Entity Relationship Diagram (ERD) and a Data Dictionary (DD), the detailed analysis of essential processes and their preliminary specification are also part of WP3. Based on the concepts of the “Structured Analysis” the analysis covers two levels of abstraction, which makes no premature decisions about how the domain will be implemented in the final system
- The essential model of the MetaDater system was modelled by capturing and describing vital aspects of the domain in focus. Taking the User Analysis (WP2) as the starting point general conceptual requirements on data, metadata and processes were analysed. This model is build by two sub models: the environmental model and the behavioral model.
- The conceptual data model for metadata, which is part of the behavioral model, is described with two modelling tools: the entity relationship diagram (ERD) and the data dictionary (DD).
Overall the challenge of the metadata management and production system is to make it possible to collect, manage and publish metadata within the frame of a unique metadata model. The planned system has also to meet the expectations of a wide variety of users and still has to warrant compatibility. It has as well to take care of involved actors and processes, which range from its collection and processing to dissemination and long term preservation. The model aims to cover metadata of most popular forms of multilingual survey designs.
The data model is compatible with the current standard of the DDI which was taken as a reference. It is extended to cover arising needs on adequate descriptions of time series survey data and international comparative studies. A specific intention of MetaDater project is to support the development of the DDI standard providing the conceptual metadata model to selected expert groups from DDI, CESSDA and other interested groups. After internal specification of some of the basic concepts a first draft will be made available to interested expert outside the project according to the following planned time schedule:
- Mid June: Presentation of the data model concept to Tom Piazza in Cologne
- July: Providing a 1st. draft to experts at DDI, CESSDA and researchers e.g. CSDI
- Autumn 2004: European expert meeting - Participation in DDI expert meetings.
The results will be the base of the programming phase for MD-PRO (WP5) and MD-COLL (WP6) as the major work in the second half of 2004.
Council of European Social Science Data Archives (CESSDA) [Transborder Data Exchange]
CESSDA is currently working on revising its transborder data exchange agreement, and has set up a working group to propose a new model. The group’s work will be reported on at this year’s IASSIST conference.
[Expert Seminar] The CESSDA expert seminar took place in Vienna hosted by WISDOM on 21-22 September 2003 and focused on “Data Service Cost Structures and User Needs: From Economic Aspects to Authentication Practices at CESSDA Archives.” Included were sessions on steps towards a new transborder agreement: fee structures, user groups, dataset types, registration and authentication procedures; and the Future of Data Processing.
The 2004 seminar will be in Neuchâtel, Switzerland 9-11 September, hosted by SIDOS, and will concern Dataset Processing and Publishing.
The East European Data Archive Network (EDAN)
Brigitte Haustein writes: [EDAN Training Seminar] The second training seminar of the East European Data Archive Network (EDAN) will be held at the University of Ljubljana (Slovenia) on 4-6 June 2004. It is intended for DDI Beginners and covers the basics of producing DDI compliant codebooks. This seminar will introduce the structure of the DDI metadata format and demonstrate how to produce DDI compliant codebooks. Based on the ADP’s experience with creating DDI-XML codebooks the participants will learn in a hands-on exercise how to get the most out of the Tag Library as well as making full use of elements and attributes. By sharing the manuals and tools for creating codebooks ADP would like to launch a discussion on Best practices in meta data production.
ERPANET / CODATA Workshop [The Selection, Appraisal and Retention of Digital Scientific Data] Excerpt from the final report Executive Summary : The international EPRANET/CODATA seminar examined the current state of practice of the selection, appraisal and retention among diverse scientific communities and discussed how archival concepts can best be applied to the management and long-term preservation of digital data. The seminar was held 15th - 17th December 2003 at the Biblioteca Nacional in Lisbon, and brought together more than sixty-five researchers, data managers, information specialists, archivists, and librarians from thirteen countries to discuss the issues involved in making critical decisions regarding the long-term preservation of the scientific record. One of the major aims for this seminar was to provide an international forum to exchange information about data archiving policies and practices across different scientific, institutional, and national contexts. The seminar proved to be extremely successful in enabling discussions between scientific and archival communities. The seminar also highlighted some conceptual hurdles to overcome before effective collaboration between the diverse communities can take place.
National Reports
BULGARIA
Brigitte Haustein writes: In 2003 the Bulgarian Social Science Data Archive was established within the Research Centre Regional and Global Development (ROGLO) in Sofia. The archive will contribute to the accessibility of survey data, development of secondary data analysis in Bulgaria and facilitate the data exchange with researchers abroad. This initiative is supported by the UNESCO Participation Programme Bulgaria. For more information, please contact Yantsislav Yanakiev (project director) reglo-office@techno-link.com
FINLAND
[FSD]
Sami Borg writes: In terms of user statistics and the progress of the major projects, the year 2003 was successful for FSD.
FSD’s Board and National Advisory Committee accepted a new organisational structure for the archive in the spring of 2003. It was implemented in the beginning of 2004. The new structure defines more clearly who has responsibility for data localisation and acquisition, user services and data documentation, and PR & information & networking activities.
In the beginning of 2004, FSD launched a three-year project which aims at creating learning materials to support social science research and methodology teaching. See more at http://www.fsd.uta.fi/tietoarkistolehti/english/13/oppimateriaali.html.
FSD began archiving qualitative data in 2003. The main challenges have been to develop anonymisation strategies, convert paper-based datasets into electronic text files, and process large open-ended Internet surveys into re-usable semi-structured datasets. XML coding was used successfully in the data processing.
The Finnish Information Centre for Register Research (ReTki) was set up in August 2003, and is part of the Finnish National Research and Development Centre for Welfare and Health (STAKES) in Helsinki. The centre focuses on facilitating register-based research in Finland, especially in social and health sciences. It also offers advice on how to plan and carry out research based on register information and on statistic reports. FSD co-operates with this new unit.
NETHERLANDS
Ron Dekker writes: In 2002 the Royal Academy of Sciences decided to dissolve NIWI, where the Steinmetz data archive is located. Next a series of commissions started to give advise on the future of NIWI and the future of data infrastructure for the Social Sciences.
Their advice of the first commission (in September 2003) pointed towards a solution in which Steinmetz Archive and the Historical Data Archive would merge, and the Research Council’s Statistical Agency would stay at the council. This would imply missing the opportunity to merge the Scientific Agency, the Steinmetz, and the Historical Data Archive into ONE strong and substantial office. Fortunately the Royal Academy decided in December 2003 to go this way. But this meant that a lot of advisory work had to be redone. It was decided (in Feb 2004) by both the Research Council and the Royal Academy to go for one new institute: DANS (Data Archiving and Networked Services). A Strategic Workforce has been appointed and 2 leading scientists (and a professional secretary) will produce a blueprint for the new organization. Decisions are expected during the summer. The new organization would start as of January 2005.
The Scientific Statistical Agency has an English version catalogue interface at http://www.dataneth.nl. Foreign researchers can order data (although it is not the researcher but the university that has to order the data).
[The Netherlands; the Steinmetz Archive and the Netherlands Historical Data Archive (NHDA)]
Helga van Gelder writes: In 2003 and 2004, both data archives are part of NIWI, the Netherlands Institute for Scientific Information Services, which is part of the Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences (KNAW).
The data infrastructure of the social sciences in the Netherlands is currently being revised. Therefore a new KNAW institute will be erected: DANS - Digital Archiving and Networked Services. A Taskforce is set up to work out the blueprint of this new institute. The expectations are that the Data Archives, Steinmetz Archive and NHDA, will continue their services in DANS.
The Steinmetz Archive The director of the Steinmetz Archive, dr. Peter van den Besselaar, is appointed professor at the University of Amsterdam from the 1st of June 2004. He has a special chair in communication and information sciences in relation to the use of ICT in the social sciences.
Cor van der Meer is seconded to the Mercator Project of the Frisian Academy until the end of 2004.
NORWAY
[NSD]
Bjørn Henrichsen writes: From its start in 1971 NSD was a part of the Research Council of Norway. After a decision in the Parliament in 2002, ownership was moved from the Research Council to the Ministry of Education and Research. In January 2003 NSD was established as a company 100 % owned by the Ministry.
The reason for the change was a wish from all parties involved to give NSD a higher degree of freedom. NSD will still receive its basic funding for the Research Council and the NSD Board will still be elected from the same constituency (mainly social sciences and medicine as well as Statistics Norway).
NSD’s agreements with Statistics Norway, the Data Inspectorate, the universities and colleges have been renewed.
It is business as usual.
ROMANIA
[RODA]
Adrian Dusa writes: In the last 6 months, RODA has been working on a Visual Access Control Unit as an add-on to the Nesstar system. Our (beta version) module is based on MySQL, Apache and Tomcat servers, and is capable of reading the published XML file with data and metadata from the Nesstar server, translates this to MySQL then print it to the webpage under a specified format (using PHP and Java Scripts). The administrator can: validate users, set various rights for users and visually set access control rules (using combo boxes with MySQL table headers). The module is completely secure, using a 128bits encryption key for usernames and passwords. As soon as we finish documenting it, we can release a working version to the community.
RUSSIA
Larisa Kosova writes: The spring 2003, the Archive’s collection was significantly replenished. VCIOM surveys for 2002 and early 2003, IKSI surveys for 2000, 2001 and 2002 are now available in free access at http://sofist.socpol.ru/oprosy.asp . The number of research available on-line reached 157.
In August 2003, special software was developed that allows calculating frequencies at our website online. One can now get a frequencies table on any question at http://sofist.socpol.ru/lin.asp .
In November 2003, the Integrated Sociological Data Archive conducted an annual seminar. Researchers and academics from Moscow and a number of regions, including Yekaterinburg, Nizhniy Novgorod, Magadan, Ufa, Kazan, Biysk, Barnaul, Ulyanovsk, Samara and Vladikavkaz attended the seminar. On the first day, the seminar participants were informed about the network that encompasses sociological data archives as well as a particular contribution of the Russian Sociological Data Archive. They also learned how to use the retrieval system, and obtained data they required for their research. The second day of the seminar was devoted to principal analytical skills one should have to handle sociological data. You can find more information at http://www.socpol.ru/archives/conference.shtml .
In November 2003, an annual congress of the American Association for the Advancement of Slavic Studies (AAASS) took place in Toronto, Canada. The Russian Sociological Data Archive was presented at a special session called “The Russian Sociological Data Archive as a New Tool for Research and Education”. For more details please visit http://www.fas.harvard.edu/~aaass .
SWITZERLAND
[SIDOS]
Dominique Joye writes: 2003 at the SIDOS
Last year could appear as a “normal year” for the SIDOS : we have complemented the datasets at disposal by adding some very interesting pieces and the distribution of the Swiss datasets is still in growth. In the same direction, we can mention an augmentation of 30% for the number of web pages asked by the users. A more complete file that documents 10 years of activities and the progress realised during this time is at disposal on the web site. Nevertheless some other points seem important to mention.
First, I have to stress the collaboration in the CESDDA and the work done around the Metadater and Madiera projects. In some sense it is a first step to-ward a major change in the work of the archives, which will be more and more part of an international network, a part of an emerging European Research Area.
Second I have to mention the Swiss participation to the international surveys, ISSP and ESS in particular, where SIDOS is responsible for. This is important for an archive in the Swiss context for three reasons:
- to learn the problems linked to the production of quality data;
- to better the image of the archive in the researcher’s community by giving quickly access to important data;
- to stress that, for these programs, the concept of infrastructure for the social sciences was introduced in a special section of the Swiss national science foundation, giving more visibility and acknowledgement to this kind of activity.
Third, 2003 was the year of introduction of a Nesstar server at the SIDOS. This point is certainly the example of new ways to service the users, with more interactivity, but is also the occasion to rethink the documentation and, in particular, to give more visibility to the complete formulation of the questions and not only the summary habitually furnished with the datasets. It is also the occasion the rethink the category of users and the way to give them access rights ac-cording their institutional situation for some datasets.
UKRAINE
Brigitte Haustein writes: Within the “Center Social Indicators” the Project of the Open Bank of Social Data (DATABANK) initiates the creation of the National Bank of Social Data. The main purpose of this project is to promote free access to data of sociological surveys about Ukrainian society in the process of transition. The following partners are co-operating in the project: Kiev International Institute of Sociology, the Sociological Department of the National University of Kiev-Mohyla Academy, Donetsk Information-Analytical Centre, Institute of Sociology of the National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine, T. Shevchenko Kyiv State University. It is expected that the completion of the DATABANK with new sociological survey data will be persistent and will not stop at this stage but will continue in the course of its existence.
UNITED KINGDOM
[EDINA]
Robin Rice writes: The EDINA National Datacentre and Edinburgh University Data Library became a planning unit in the University’s Information Services Group, no longer a division in the Computing Service. EDINA added the Educational Image Gallery to its suite of multimedia content services, updated its UKBORDERS boundary data service with 2001 data, and became further involved with a number of technical development projects, from geographic metadata to middleware infrastructure services. It hosted its first EDINA Exchange public event in May, showcasing its projects and services for site representatives at the National e-Science Centre in Edinburgh. (edina.ac.uk)
EDINA also participated in a consortium bid to host a UK Digital Curation Centre and is now involved in the management of the set-up phase as well as hosting a website and helpdesk for the Centre. The DCC intends to support expertise and practice in data curation and preservation, prompting collaboration between the Universities and the Research Councils to ensure that there is continuing access to data of scholarly interest. The initial focus is on research data, but the policy intention is to also address the preservation needs of e-learning and scholarly communication. (www.dcc.ac.uk)
A group of university-based data librarians and data managers have come together to form a support group - DISC-UK, or Data Information Specialist Committee-United Kingdom. They plan to meet 3-4 times per year to compare issues and solutions in their daily work, and met for the first time at the London School of Economics in February, this year. The founding members - six data professionals from Oxford, Edinburgh, and LSE - intend to open up their group to others performing similar roles in their universities, such as national data service site representatives - though they may not work in dedicated data libraries. An initial website for the group has been set up, with links to member sites and a description of the group’s aims at, http://datalib.ed.ac.uk/disc-uk/
[ESDS]
Kevin Schürer writes: The initial period of the new Economic and Social Data Service (ESDS - established in January 2003) was hectic but exciting. Clearly, three key objectives in the initial period were to establish effective communication between the separate units of the distributed service (two at University of Essex and two at University of Manchester); to establish an identity for the new service; and at the same to continue service the user community.
Whilst services to users continued uninterrupted from January, the new service was formally launched on 30 June 2003 at an event held at Regent’s College, London, at which various new products were demonstrated and Ian Diamond (Chief Executive, Economic and Social Research Council) and Len Cook (the National Statistician) gave addresses. This meeting also provided the opportunity for the first meeting of the ESDS Advisory Committee to take place, under the chairmanship of John Pullinger (Office for National Statistics).
The new ESDS website went live and has been continuously populated with new content reflecting the four new value-added subject-oriented services, in addition to the core Access and Preservation and Management services, which make up ESDS. The new online data delivery system for international macrodata using Beyond 20/20 went live in April 2003. A new Athens-based registration service for ESDS International was developed, tested and was launched in June 2003, in order to augment the web-based Beyond 20/20 delivery system and the NS Times Series Databank. This will provide the basis of the service-wide one-stop registration system to be implemented in June 2004.
In order to promote and raise user awareness about the new service a lot of effort was placed on organising and contributing to a number of meetings, training events; seminars and workshops. While some of these events, due to the audience in question, focused on one or other of the specialist services of ESDS, all provided general contextual information on ESDS and its component services.
Over the third quarter a large amount of work took place on internal systems development, building the ESDS administrative back-end. This is largely invisible to the outside world, yet is critical to the smooth functioning of the service. An overview of these developments is summarised at follows:
- A complete re-vamping of the process by which users register, order data, and are charged is underway, together with a complete restructuring of the central user and order database. New system to be launched end June 2004.
- New procedures regarding the acquisition process are well advanced, with new interactive deposit forms, new depositor licence, new back-end database for depositors and acquisitions negotiations.
- A new suite of input programs for the new catalogue have been implemented and new cataloguing QA procedures have been put in place. These will greatly speed and improve quality of cataloguing.
- Development of a new data processing tracking database, which will directly feed the UKDA-produced metadata (catalogue metadata, read files, citation and title page information).
- Automation work was undertaken to speed, smooth, and standardise the preparation of datasets in multiple software formats for http download.
- Work is being done on access control will allow more users to access more datasets via http download (i.e. “depositor permission” datasets will be able to be mounted, non-academic users will be able to use download if access conditions permit, etc).
- Work is being done on Athens implementation, and on becoming an Athens issuing agent for users outside UK HE/FE who can’t obtain Athens IDs through their home institution, and on implementing Athens in Nesstar access control.
- SLD (Service Level Definition) has finally been agreed at videoconference on 22 October. Rationalised and streamlined reporting template will make quarterly reporting against target performance indicators more straightforward.
- ESDS International have been successful in negotiating draft licences with the UN for the UN Common Database, with World Bank for the World Development Indicators and Global Development Finance data and with the ILO for the Key Indicators of the Labour Market data series. OECD have also agreed to increase the number of data cells that can be extracted via the Beyond 20/20 WDS to 50,000.
Another strand of ESDS activity that we would wish to highlight is the continued acquisition of new data collections. Since the establishment of ESDS in addition to ‘core’ and longitudinal data materials the ESDS Access and Preservation has acquired a total of 63 government datasets (excluding new editions). This figure is 80 per cent in excess of the originally set target. Equally, the ESDS International data portfolio has expanded considerably in the last quarter with the addition of a number of key international macro databanks.
Lastly, another highlight in this period has been the development by ESDS International (hosted at MIMAS, University of Manchester) of an interactive web-based data exploration and visualisation interface to a set of key international statistics. CommonGIS, a web-based Geographical Information System (GIS), has been used to provide a pilot interface to the freely available CIA World Factbook 2002 socio-economic data. During 2004 this value-added service will be enhanced to provide users the chance to explore and view themed datasets from the ESDS International data portfolio using the interactive web GIS.
Over the course of 2003, ESDS had approximately 2,000 distinct users, who collectively accessed approximately 17,000 data collections.
 {width=“465”
height=“279”}
{width=“465”
height=“279”} {width=“464”
height=“279”}
{width=“464”
height=“279”}